Tech Multiples Decline: Ripple Effects in Private Sector
By Lior_Ronen | Founder, Finro Financial Consulting
Over the past few years, the tech sector has emerged as a prominent driver of global economic growth, captivating investors with its soaring revenue multiples.
However, a significant shift has recently occurred, causing a decline in tech stock revenue multiples.
In fact, the median revenue multiple plummeted from 19.04x in December 2020 to 6.31x in April 2023, as depicted in the chart below.
This sudden change has raised concerns among investors and market observers, prompting questions about the reasons behind this trend and its implications for private tech companies.
In this article, we delve into the factors contributing to the shrinking tech stock revenue multiples and explore how this development may impact the valuations of private tech companies.
We have divided the article into three main sections:
The Decline in Revenue Multiples.
Factors Behind the Drop.
Implications for Private Tech Company Valuations.
By examining these topics, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the tech sector and its ramifications for investors and other market participants.
The decline in revenue multiples
Before delving into the decline of revenue multiples in the tech industry, it is important to understand what exactly a revenue multiple represents.
The revenue multiple, also known as the EV/Revenue ratio, is the ratio between an enterprise value (EV) and its annual revenue. It serves as a valuable metric for comparing the relative value of companies within the same industry.
Traditionally, the tech sector has commanded higher revenue multiples compared to other industries, reflecting investor enthusiasm and the growth potential of technology-driven businesses.
However, the recent downward trend in revenue multiples indicates a shift in market sentiment, raising uncertainties about the sector's future trajectory.
To gain a better understanding of the current trend, it is essential to contextualize the decline in revenue multiples by comparing it with historical data.
In the past, tech stocks typically enjoyed higher multiples, often in the double digits, as investors were willing to pay a premium for anticipated future growth.
The dot-com bubble in the late 1990s and early 2000s serves as a prime example, where exuberance and speculation led to sky-high valuations in the sector.
However, the current decline in revenue multiples signifies a departure from these historical norms, suggesting that investors have adopted a more cautious and discerning approach to the tech sector.
Several factors contribute to this shift in investor sentiment, including rising interest rates, market saturation, regulatory concerns, and evolving risk preferences.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into these factors, exploring their potential impact on the valuations of private tech companies.
Factors contributing to the decline: Increasing Interest Rates
One of the prominent factors driving the decline in tech stock revenue multiples is the rise in interest rates.
As central banks tighten monetary policies in response to inflationary pressures and economic recovery, borrowing costs increase, highlighting the opportunity cost of investing in high-growth tech stocks.
We will discuss the role of Federal Reserve policy in shaping interest rates and how these changes impact the valuation of tech stocks.
1. Federal Reserve Policy
The increase in interest rates is primarily driven by the Federal Reserve tightening its monetary policy in response to economic conditions.
As borrowing costs rise, it becomes more expensive for tech companies to finance their growth, reducing the present value of future cash flows.
This factor plays a significant role in affecting the valuation of tech stocks.
2. Impact on Tech Stocks and Valuation
Tech stocks, with their higher growth expectations and longer time horizons for profitability, are particularly sensitive to interest rate changes.
Rising interest rates increase the opportunity cost of investing in tech stocks, prompting investors to seek alternative investments with better risk-adjusted returns.
Consequently, the demand for tech stocks decreases, leading to lower valuations and revenue multiples.
Factors contributing to the decline: Market Saturation and Competition
Market saturation and increasing competition within the tech sector are key factors contributing to the decline in tech stock revenue multiples.
As the industry matures and more players enter the market, growth rates may slow down, posing challenges for companies to maintain market share and profitability.
Let's examine the impact of market maturity and growing competition, particularly from emerging markets, on tech stock valuations.
1. Maturity of the Tech Sector
As the tech sector reaches maturity, many companies encounter a saturation point in their core markets.
With more firms competing for the same customers, the potential for revenue growth diminishes.
Additionally, as companies grow in size, sustaining the rapid growth rates observed during the early stages becomes more challenging.
These factors have led to more moderate growth expectations and reduced investor enthusiasm, ultimately contributing to the decline in revenue multiples.
2. Increased Competition from Emerging Markets
The rise of tech companies from emerging markets has further intensified the impact on revenue multiples.
These firms, characterized by lower cost structures and agile business models, have become highly competitive on a global scale.
By offering products and services at lower prices, they have exerted pressure on established tech companies.
This competitive pressure has forced incumbents to reduce prices or increase innovation to remain competitive. Consequently, established firms have experienced a squeeze on their revenue and profit margins, leading to lower valuations and a decline in revenue multiples.
Moreover, the growing influence of emerging market tech companies has restricted expansion opportunities for established firms, impeding potential revenue growth.
By examining these factors, we gain a better understanding of the challenges faced by tech companies and their impact on revenue multiples.
In the following sections, we will continue to explore the remaining factors: regulatory concerns and investor sentiment and risk aversion.
Factors contributing to the decline: Regulatory concerns
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples is also influenced by the increasing concerns surrounding regulatory issues faced by the sector.
As large tech companies have attained market dominance, governments and regulatory bodies have intensified their scrutiny of their business practices, leading to regulatory actions.
Let's delve into the impact of antitrust and privacy issues, as well as the broader implications of government intervention in the tech sector.
1. Antitrust and privacy issues
In recent years, regulatory scrutiny has heightened over the market dominance and data privacy practices of large tech companies.
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have become more proactive in overseeing the tech sector due to concerns about anticompetitive behavior and potential violations of user privacy.
This regulatory environment has introduced uncertainty for tech companies, as the possibility of fines, sanctions, and forced divestitures looms.
Such uncertainty can negatively impact investor sentiment, leading to lower valuations and a decline in revenue multiples.
2. Government intervention in the tech sector
The growing involvement of governments in regulating the tech sector raises concerns about increased barriers to entry and reduced growth opportunities for tech companies.
Regulatory interventions may result in higher compliance costs for businesses and necessitate changes to their business models to meet new requirements.
These added burdens can affect profitability and growth potential, contributing to lower revenue multiples.
Furthermore, as governments adopt more protectionist policies and impose restrictions on cross-border data flows, tech companies may face challenges in expanding their global footprint and accessing new markets.
These restrictions limit the growth prospects of tech firms and further contribute to the decline in revenue multiples.
By exploring these factors, we gain a better understanding of the impact of regulatory concerns on tech companies and their influence on revenue multiples.
In the following sections, we will continue to examine the remaining factor: investor sentiment and risk aversion.
Factors contributing to the decline: investor sentiment and risk aversion
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples can also be attributed to a shift in investor sentiment and risk preferences.
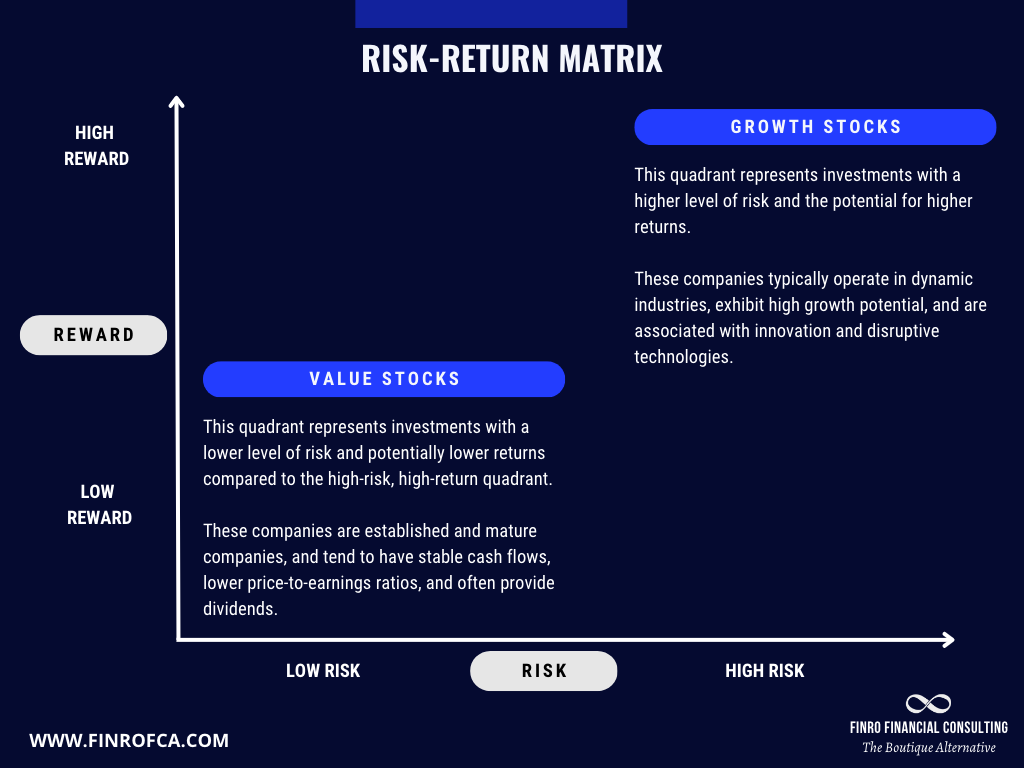
As the global economic outlook becomes more uncertain, investors tend to adopt a more cautious approach to high-growth tech stocks, instead favoring more conservative investments or value stocks with stable cash flows and dividends.
Let's explore the implications of this changing market sentiment on the performance of growth and value stocks and the broader impact on tech stock valuations.
1. Shift in Market Preferences
During periods of economic uncertainty, investors often exhibit increased risk aversion. They seek out investments perceived as safer and more reliable. This change in sentiment leads to a rotation out of high-growth tech stocks and into more conservative options, such as value stocks, bonds, or other assets offering predictable returns. Consequently, the decreased demand for tech stocks contributes to lower valuations and a contraction in revenue multiples.
2. Impact on Growth vs. Value Stocks
The shift in investor sentiment has resulted in a relative underperformance of growth stocks, including tech stocks, compared to value stocks. While value stocks typically exhibit lower revenue multiples and slower growth rates, they offer greater stability and income potential through dividends.
These characteristics make value stocks more attractive to risk-averse investors during uncertain times.
As investors reallocate their portfolios in favor of value stocks, the revenue multiples for tech stocks contract, reflecting the market's changing risk appetite and valuation preferences.
By understanding the impact of investor sentiment and risk aversion, we gain insights into the shifting dynamics that contribute to the decline in tech stock revenue multiples.
In the following sections, we will continue to explore the remaining factors: regulatory concerns and their influence on tech stock valuations.
Effects on private tech company valuations: challenges in raising capital
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples not only impacts public companies but also creates significant challenges for private tech companies seeking to raise capital.
As investors become more cautious and valuations in the public markets contract, the fundraising environment for private firms becomes increasingly difficult.
Let's explore the effects of these market dynamics on venture capital investment trends and the implications for early-stage startups.
1. Venture Capital Investment Trends
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples in the public markets influences venture capital (VC) investors' approach to funding private tech companies.
VC firms may become more cautious, leading to tighter investment criteria and reduced valuations for early-stage startups seeking funding. Furthermore, as VC firms experience lower returns on their public market investments, they may have limited capital available for new ventures.
This constraint further restricts the fundraising environment for private tech companies.
2. Impact on Early-Stage Startups
Early-stage startups heavily rely on external funding to fuel their growth.
However, a decline in tech stock revenue multiples can significantly affect their ability to secure necessary capital.
As investors become more risk-averse, they may demand higher equity stakes in exchange for funding, posing challenges for entrepreneurs in maintaining control over their companies and executing growth strategies.
Consequently, private tech firms may face slower growth trajectories and potential impacts on their long-term success.
By exploring these effects, we gain a better understanding of the challenges faced by private tech companies in raising capital.
In the following sections, we will continue to explore other aspects related to the decline in tech stock revenue multiples and its broader implications.
Effects on private tech company valuations: exit strategies and potential market impact
The changing landscape of tech stock valuations can have significant implications for the exit strategies of private tech companies. Whether pursuing an initial public offering (IPO), direct listing, or merger and acquisition (M&A), the decline in revenue multiples can alter the outcomes and valuations of these transactions. Let's discuss how these exit strategies may be affected and the potential market impact of these changes.
1. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) and Direct Listings
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples can impact the exit strategies of private tech companies planning to go public. Lower public market valuations may make it challenging for private firms to achieve their desired valuations in an IPO or direct listing. This can lead to delayed offerings, downsized deals, or a higher preference for alternative exit strategies, such as mergers and acquisitions.
2. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
As public market valuations decline, private tech companies may become attractive acquisition targets for larger firms seeking to expand their portfolios or acquire innovative technologies. However, the lower revenue multiples may also result in lower acquisition prices, potentially impacting the returns for private company investors and founders.
By exploring these effects, we gain a better understanding of how changing tech stock valuations influence the exit strategies pursued by private tech companies. In the following sections, we will continue to explore the broader implications of these changes and their potential market impact.
Effects on private tech company valuations: Valuation Methodologies
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples and the increase in interest rates can also influence the valuation methodologies used to value private tech companies. As market conditions change, the assumptions and inputs used in common valuation techniques, such as comparables analysis and discounted cash flow, may need to be adjusted. In this section, we will explore the implications of these changes on private tech company valuations.
1. Comparables analysis and the decline in revenue multiples
As the revenue multiples for public tech companies contract, the implications for private tech company valuations become apparent, particularly in the comparables method.
The comparables valuation method involves comparing a private company's financial metrics and valuation multiples to those of similar public companies. As public tech stock valuations decline, the valuation multiples used in comparables analysis will also decrease, leading to lower valuations for private tech companies.
2. Discounted cash flow (DCF) and the impact of interest rates
The discounted cash flow (DCF) method, another common valuation technique for private tech companies, is also affected by the decline in tech stock revenue multiples and the increase in interest rates. The DCF method relies on discounting the future cash flows of a company to their present value using an appropriate discount rate. As interest rates rise, the discount rate used in the DCF analysis also increases, reducing the present value of future cash flows and resulting in lower valuations for private tech companies.
Conclusion
The decline in tech stock revenue multiples is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by economic, competitive, regulatory, and market sentiment factors. As these forces converge, they create a challenging environment for tech companies, both public and private, affecting valuations, growth prospects, and access to capital.
Private tech companies, in particular, face a range of challenges as they navigate this new landscape, from raising capital and pursuing exit strategies to adjusting valuation methodologies in response to changing market conditions.
While it is difficult to predict the future trajectory of tech stock valuations, investors, entrepreneurs, and other stakeholders must remain vigilant and adapt to these shifting market dynamics.
By understanding the factors driving the decline in revenue multiples and their implications, market participants can make more informed decisions, better manage risk, and ultimately capitalize on the opportunities that may arise in the evolving tech landscape.