Simon Reid
Co-Founder & Managing Director, Darvis UK
By Lior Ronen | Founder, Finro Financial Consulting
Financial modeling is a cornerstone in the startup environment, providing critical insights that drive strategic decision-making.
For startups, where resources are often limited and the market dynamics are volatile, having a robust financial model is not merely beneficial—it's crucial.
This tool does more than crunch numbers; it enables founders and business leaders to visualize the future financial landscape, gauge the viability of their business strategies, and communicate value to potential investors.
This article aims to demystify the process and benefits of financial modeling for startups.
We will explore what a startup financial model entails, dissect its core components, and illustrate how effectively it can guide your company through the complexities of growth and investment.
Whether you are gearing up for a funding round or planning your next big market move, understanding how to leverage a well-crafted financial model can set the stage for sustained success.
A startup financial model is a comprehensive framework that startups use to forecast their financial health and project their economic future.
This model integrates various financial data—such as projected revenues, expenses, and cash flows—to create a detailed picture of a startup’s financial trajectory over a specified period, typically ranging from 12 to 36 months.
The primary function of a startup financial model is to serve as a forecasting tool.
It allows founders and financial analysts to anticipate future financial results based on current plans and assumptions.
But beyond mere predictions, the model is pivotal for strategic planning, helping startups navigate the uncertainties of business growth and market dynamics.
The users of startup financial models are diverse. They include startup founders, CFOs, financial analysts, and potential investors.
For founders and company executives, these models are instrumental in making informed decisions about resource allocation, pricing strategies, and growth pathways.
Investors, on the other hand, use these models to evaluate the financial viability and potential return on investment of the startup, which is crucial during fundraising stages.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of a startup financial model makes it exceptionally valuable. As startups operate in environments where market conditions are continually evolving, the flexibility to integrate new data and refine forecasts is vital.
This adaptability ensures that the model remains relevant and provides actionable insights, even when external economic conditions change or internal business strategies are adjusted.
In preparing for the detailed exploration of a startup financial model, it's important to understand its core components, which we will delve into next. These components typically include:
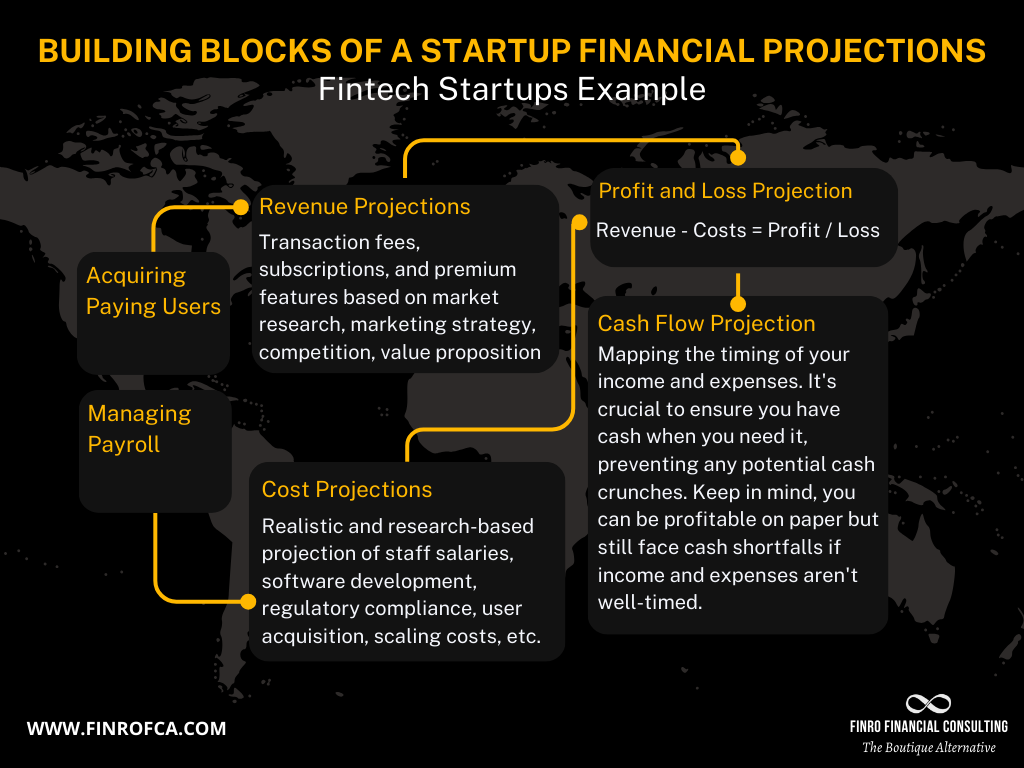
Projected Financial Statements: These give a future view of the financial health of the company, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Revenue Projections: Detailed predictions of future sales based on market analysis and business initiatives.
Expense Forecasts: Estimations of upcoming costs, categorized into fixed and variable expenses.
Payroll and Headcount: Plans for employee growth and salary allocations, reflecting the company's scaling strategy.
Each component plays a critical role in painting a complete picture of a startup's financial future, helping stakeholders make better-informed decisions.
As we transition into the next section, we'll unpack these components in detail, exploring how each contributes to the robust framework of a startup financial model, ensuring stakeholders can make informed, data-driven decisions that align with the company's financial and strategic goals.

Building on our understanding of the overarching framework of a startup financial model, let's now delve into its core components.
These elements form the backbone of financial forecasting and are crucial for creating a realistic portrayal of a startup’s future financial landscape.
Projected Financial Statements
The cornerstone of any financial model is its projected financial statements, which include the income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet:
Income Statement: This statement forecasts a startup's profitability over a specific period. It shows expected revenues and expenses, helping stakeholders understand potential profits or losses.
Cash Flow Statement: Essential for managing liquidity, this statement tracks the flow of cash in and out of the business. It helps predict future cash positions, which is crucial for operational and strategic decision-making.
Balance Sheet: Offering a snapshot of the company's financial standing at various future points, the balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity. It’s vital for assessing the company’s solvency and financial stability.

Detailed Projections
The financial model also includes detailed projections that further refine the company's financial forecast:
Revenue Projections: These are typically based on a combination of historical data, market analysis, and sales strategies. Revenue projections consider factors such as market demand, pricing strategies, and competitive positioning to forecast sales figures.
Expenses: Accurate expense forecasting is critical for maintaining financial health. Expenses are divided into fixed and variable costs. Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of business activity, such as rent and salaries, while variable expenses fluctuate with sales volume, like materials and production costs.
Payroll and Headcount: Workforce planning is an integral part of financial projections, particularly for growing startups. This section outlines anticipated changes in headcount and payroll expenses as the company scales, aligning with strategic growth objectives and market opportunities.
Understanding these components in detail enables stakeholders to grasp the financial nuances of the startup and prepares them for more strategic roles in decision-making.
As we move forward, the next section will explore the strategic benefits of a startup financial model. We'll see how these detailed components not only support everyday business operations but also empower startups in strategic decision-making, investor relations, and performance management.
Having explored the core components of a startup financial model, it’s important to understand how these elements translate into strategic advantages.
Financial models are not just about numbers and projections; they are vital tools that can drive significant business outcomes.
Investor Attraction
A well-structured financial model is a key asset in attracting and convincing investors.
It demonstrates the startup's potential for growth and profitability in a quantifiable manner, showcasing the business's fiscal discipline and foresight.
Investors look for detailed, realistic financial projections that highlight a clear path to revenue generation and cost management.
By presenting a thorough financial plan, startups can instill confidence in investors, showing that the venture is managed by a team that understands its financial commitments and objectives.
Risk Management and Opportunity Identification
Financial models play a crucial role in risk management and opportunity identification.
They allow startups to foresee potential financial challenges and market dynamics that could impact their business. By analyzing various scenarios, such as shifts in market demand or changes in cost structures, startups can identify risks early and devise strategies to mitigate them.
Similarly, these models can reveal lucrative opportunities—whether it's a gap in the market, potential for cost savings, or an area for expansion. This foresight enables startups to pivot their strategies effectively, capitalizing on opportunities while avoiding pitfalls.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is critical for the growth and sustainability of any startup. Financial modeling provides a framework for allocating resources wisely—ensuring that investments are made in areas that offer the highest returns.
Whether it's deciding how much to spend on marketing, where to invest in product development, or how to manage operational costs, a financial model helps leaders make informed decisions.
This strategic allocation of resources is crucial for maximizing profitability and ensuring long-term success.
As we have seen, financial modeling extends beyond mere financial management. It impacts various aspects of business strategy, from securing investments and managing risks to optimizing resource deployment.
In the following section, we will delve deeper into the practical applications of financial modeling, demonstrating how it supports decision-making across different business areas and scenarios.
The strategic benefits of financial modeling are complemented by its practical applications, which directly impact daily management and long-term planning.
This tool is instrumental in scenario planning, performance tracking, and supporting crucial business decisions.
Scenario Planning
Scenario planning within financial modeling allows startups to prepare for various potential business conditions by simulating different financial outcomes.
By creating multiple scenarios—such as best-case, worst-case, and most likely scenarios—startups can visualize the financial impacts of different market conditions, economic environments, or strategic choices.
This proactive approach helps business leaders understand potential risks and rewards, enabling them to make adjustments to their strategies before changes in conditions force their hand.
For instance, a startup might explore the financial effects of a new competitor entering the market or the impact of a global economic downturn, ensuring they are prepared for any eventuality.

Performance Tracking and Management
Financial models are also vital for setting benchmarks and tracking the company’s performance against these markers.
By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) within their financial models, startups can monitor progress and evaluate efficiency across different departments and projects.
This regular monitoring helps identify areas where the business is over or under-performing, allowing for timely adjustments in tactics.
For example, if revenue from a new product line is not meeting projections, the model will highlight this discrepancy, prompting a reassessment of product marketing strategies or pricing structures.

Decision Support
One of the most significant applications of financial modeling is its role in supporting critical business decisions.
With comprehensive data and projections at their fingertips, business leaders can make informed decisions about market expansion, resource allocation, and cost-cutting measures, among others.
For example, a detailed financial model might reveal that expanding into an overseas market could dramatically increase profitability based on demand forecasts and cost estimates.
Conversely, it could show that cutting down on certain operational expenses would stabilize cash flow during a slow growth phase. Such insights ensure that decisions are not based on hunches but are backed by data-driven analysis.
Creating a financial model that accurately reflects the complexities of a startup involves careful consideration, attention to detail, and the right tools.
Here are some key aspects to consider, common pitfalls to avoid, and resources that can assist in building a robust financial model.
Key Considerations
The financial model should reflect the startup’s business model, market conditions, and the stage in which the startup is. So when developing a financial model, several key considerations should be prioritized to ensure its effectiveness and reliability:
Startup Stage Awareness: Tailor the financial model to the specific lifecycle stage of the startup. For early-stage startups, focus might be on burn rate and cash runway, while growth-stage companies might emphasize scalability and profitability metrics. This consideration ensures the financial model is relevant and practical for current needs and future projections.
Startup Stage Awareness: Tailor the financial model to the specific lifecycle stage of the startup. For early-stage startups, focus might be on burn rate and cash runway, while growth-stage companies might emphasize scalability and profitability metrics. This consideration ensures the financial model is relevant and practical for current needs and future projections.Realistic Assumptions: The foundation of any financial model is the assumptions upon which it is built. Ensure these assumptions are realistic and based on thorough market research, historical data, and industry benchmarks.
Sensitivity Analysis: Incorporate sensitivity analysis to understand how changes in key assumptions impact your financial outcomes. This analysis helps in identifying which variables have the most influence on your model’s outputs and can guide where to focus risk management efforts.
Granularity: While it might be tempting to keep the model simple, appropriate granularity in projections—such as monthly cycles rather than annual ones—can provide more accurate and actionable insights.
Integration with Business Activities: Ensure the financial model aligns with business activities and timelines. It should reflect the strategic goals and be capable of adapting as those goals evolve.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Several common pitfalls can undermine the effectiveness of a financial model if not carefully managed:
Over-optimism: Entrepreneurs often fall into the trap of overly optimistic projections. Temper optimism with realism to ensure that your model remains practical and believable.
Ignoring Cash Flows: It’s crucial not to focus solely on profitability but to give adequate attention to cash flow management, as cash constraints are often the biggest threat to a young startup.
Complexity Overkill: While detail is important, overly complex models can become unmanageable and obscure rather than clarify financial insights. Strive for simplicity where possible without compromising on necessary details.
Tools and Resources
Several tools and resources can help streamline the process of building and maintaining a financial model:
Software Solutions: Tools like Excel remain popular for financial modeling due to their flexibility and widespread use. For more sophisticated needs, software like Quantrix or PlanGuru can offer additional functionalities tailored to financial forecasting.
Templates and Examples: Utilize templates from sources like the Corporate Finance Institute or download examples from platforms like Smartsheet to get a head start on your model.
Professional Guidance: Especially for founders without a finance background, consulting with financial analysts or using advisory services can be invaluable. Services such as SCORE or local startup incubators often offer free or low-cost guidance.
Setting out in the tech world without a solid financial model is like exploring a new city without a map.
This analogy may seem dramatic, but it vividly captures why a detailed and dynamic financial model is crucial for any tech startup.
It's not merely about having numbers arranged on a spreadsheet; it's about understanding where your business could be heading and strategizing accordingly.
Here's what some of our clients have to say about the impact of financial modeling on their ventures:

Simon Reid
Co-Founder & Managing Director, Darvis UK
I have worked with Lior at #Darvis, an AI powered technology company, where Lior worked with us to develop a financial model, review pricing structures, cash flow needs and general financial information. Lior is always insightful, responsive, professional and resourceful, which are key attributes when working with rapid paced entrepreneurial companies. Lior is really effective at helping organisations development the necessary financial forecasting and management tools needed to grow successfully and attract new investment. I would strongly recommend Lior to new clients.

Isaac Litman
Founder and CEO, Neteera
I worked with Lior and with Finro to build a financial model for our seed round. Lior meticulously led the forecasting process, analyzing our activity, mapping all aspects of our business, and immaculately creating our 5-years all-around financial model that fits our needs.
The Finro team quickly understood the technology, details of the business, and the primary growth factors, successfully implementing them in the model.
Overall a high-quality and seamless experience that I recommend to every startup founder!
These testimonials highlight not just the functional utility of financial models but also underscore their strategic value.
Financial models serve a dual purpose: guiding internal financial strategy and impressing potential investors or partners during funding rounds or M&A discussions.
Given their importance, the real consideration is what kind of expertise you want behind this crucial tool. Why navigate the complexities of tech financial modeling without the insights and experience a specialized partner can provide?
As we continue, we'll break down the advantages of a tailored approach to financial modeling for tech startups.
From ensuring accuracy to aligning with what investors want to see, we'll explore how the focused expertise of financial modeling experts like Finro can make all the difference in positioning your startup for success.
Adopting a generic approach to financial modeling is typically not a good idea for technology startups.
Their unique challenges and market dynamics demand a specialized approach to financial modeling—one that accurately reflects their business model and adapts to rapid market and technology changes.
Structured Process for Comprehensive Coverage
Specialized financial modeling firms utilize a structured, thorough process tailored to address every aspect of a startup’s operations.
This method ensures comprehensive coverage, from detailed revenue streams and cost structures to market dynamics and growth projections.
Building a model that captures the full complexity of your startup ensures that your financial plans are robust and detailed.
Expertise in the Tech Sector
The tech industry is marked by swift innovation and changing consumer demands, necessitating partners who possess deep sector-specific knowledge. Firms specializing in financial modeling bring this expertise, which is crucial for making accurate financial predictions in a volatile market.
Their deep understanding allows these firms to create financial models that not only reflect the true nuances of tech businesses but also resonate with industry realities.
Insight into Investor Expectations
Understanding investor preferences requires both art and science. Specialized financial modeling firms have extensive experience with investors in the tech ecosystem, providing crucial insights that shape financial models to meet investor expectations effectively.
Whether it's showcasing your business's scalability, the soundness of your revenue model, or your potential for market leadership, these firms excel at emphasizing the elements most likely to attract investor support.
Navigating Complex Financial Planning and Investor Negotiations
Selecting the appropriate financial modeling partner is crucial for tech startups as they manage complex financial planning and engage with investors.
The risks associated with do-it-yourself or general financial modeling approaches, such as oversights and misalignment with investor interests, underscore the importance of choosing a specialized partner.
With a solid history in the tech sector, specialized financial modeling firms can help startups sidestep these pitfalls, ensuring that their financial models are not only accurate but also strategically aligned with their long-term objectives.
For tech startups, financial modeling transcends simple tactical exercises; it is a strategic initiative that bridges the gap between innovative concepts and lasting business success.
By partnering with a specialized financial modeling firm, like Finro, startups ensure that their financial strategies are crafted with precision and align with both internal ambitions and external investor expectations.
As the tech industry evolves, maintaining a reliable, insightful financial model will continue to be a cornerstone of strategic planning and investment readiness, establishing a strong foundation for growth and success.
As we've explored throughout this article, financial modeling is an indispensable tool for tech startups, essential not only for internal strategic planning but also for securing external engagements like investor funding and navigating mergers and acquisitions.
The complexity and rapid evolution of the tech industry demand more than just rudimentary financial projections; they require a deep, nuanced understanding of market dynamics, technology trends, and investor expectations.
Choosing the right financial modeling partner is critical. Startups need experts who not only bring a detailed, analytical approach to financial projections but also a strategic mindset that aligns with the startup's long-term goals.
The risks of opting for generalized or DIY financial modeling approaches—such as potential oversights or misalignment with investor interests—are too significant to ignore.
These risks underscore the necessity for specialized expertise that can navigate the unique challenges of the tech sector.
In summary, the right financial modeling can mean the difference between merely surviving and truly thriving in the competitive tech landscape.
By leveraging detailed, expertly crafted financial models, tech startups can gain the clarity and confidence needed to make informed decisions that drive growth and success.
As the business world continues to evolve, embracing the power of sophisticated financial modeling remains a pivotal strategy for any startup aiming to make a significant impact in its industry.
Importance of Financial Models: Essential for strategic planning, risk management, and investor relations in startups.
Dynamic and Adaptable: Models must update with new data and market changes to stay relevant.
Detailed Components: Includes projections for income, expenses, payroll, and headcount.
Strategic Benefits: Helps attract investors, manage resources, and identify risks and opportunities.
Specialized Expertise Required: Tailored financial modeling enhances accuracy and aligns with investor expectations.