Sell-Side vs. Buy-Side Due Diligence: Know The Differences
By Lior Ronen | Founder, Finro Financial Consulting
Whether you're buying a company, merging with another, or selling your own, there's a crucial step you can't skip: due diligence.
Think of it as doing a thorough check-up on a used car before you decide to buy it.
You'd want to know everything, from how well it runs to any hidden issues that could become headaches later.
Similarly, in business, due diligence is your way of getting under the hood to understand exactly what you're getting into.
This process isn’t just a quick look at the company’s finances or a brief chat with the management team. It’s a comprehensive review of the financial health, operational efficiencies, legal standings, and so much more.
Essentially, it's the detailed investigation you do to protect your investment and ensure there are no surprises after the deal is done.
Now, there are two main types of due diligence: buy-side and sell-side. Each plays a crucial role from different sides of the table.
Buy-side due diligence is what you do when you’re considering buying a business. It’s all about verifying what the seller has told you and making sure the business fits with your goals and expectations.
It’s your way of checking that the investment is sound and the business is as good as it seems.
On the other hand, sell-side due diligence is when you’re selling or looking to attract investors.
This is your chance to clean up and organize everything, ensuring your business looks its best. It’s about being upfront and clear so no deal-breakers are lurking in the shadows.
Grasping the ins and outs of both buy-side and sell-side due diligence is vital for anyone in the business transaction game.
It not only helps you navigate through the complexities but also arms you with the information needed to make decisions that are both smart and strategic.
Due diligence is a pivotal element in business transactions, serving as the bridge between potential risks and opportunities for both buyers and sellers. On the buy-side, it's about conducting a thorough investigation to protect investments, identifying any potential financial, operational, or legal issues before finalizing a deal, and uncovering strategic growth opportunities.
Conversely, sell-side due diligence is initiated by sellers aiming to showcase their business in the best light, addressing any issues upfront to enhance the company's value and attract the best offers. This preparatory work not only facilitates smoother transactions but also ensures that both parties can achieve a mutually beneficial agreement, underpinning the strategic alignment and long-term success of the acquisition or sale.
- Understanding Buy-Side Due Diligence
- Definition of Buy-Side Due Diligence
- Buy-Side Due Diligence: Key Preparation Steps
- Benefits of Thorough Buy-Side Due Diligence
- Exploring Sell-Side Due Diligence
- Definition of Sell-Side Due Diligence
- Sell-Side Due Diligence: Key Preparation Steps
- Advantages of Conducting Sell-Side Due Diligence
- Key Differences Between Buy-Side and Sell-Side Due Diligence
- Conclusion
Understanding Buy-Side Due Diligence
Definition of Buy-Side Due Diligence
Buy-side due diligence is an essential investigative process conducted by potential buyers or investors to assess the viability and value of a target company.
While traditionally aimed at identifying financial discrepancies, legal issues, and operational inefficiencies—often referred to as red flags—the scope of due diligence has evolved. Today, it equally emphasizes uncovering growth opportunities that can drive future value.
This comprehensive approach involves a meticulous review of not just the company's financial records and legal documents but also its market position, competitive landscape, operational processes, and strategic fit within the buyer's portfolio.
The purpose extends beyond safeguarding against potential risks to include identifying pathways for cost savings, new revenue streams, and strategic synergies that can enhance the investment's return.
In essence, modern buy-side due diligence serves a dual role: protecting the buyer from unforeseen liabilities and equipping them with a detailed understanding of how the acquisition can contribute to their strategic growth objectives.
This dual focus ensures that buyers are not just avoiding pitfalls but are also investing in opportunities that align with their long-term vision and growth plans.
| Aspect | Traditional Role | Growth-Focused Role |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Identify and mitigate potential risks and red flags. | Uncover growth opportunities and strategic synergies. |
| Focus Areas | Financial discrepancies, legal issues, operational inefficiencies. | Market expansion, revenue streams, cost savings, strategic fit. |
| Outcome | Safeguard against unforeseen liabilities and ensure a sound investment. | Enhance investment return through strategic growth opportunities. |
| Approach | Defensive, ensuring the target company has no hidden problems. | Proactive, seeking ways the acquisition can add value to the buyer’s portfolio. |
| Value | Minimizes potential losses and protects the buyer's investment. | Maximizes potential gains and aligns with the buyer's growth objectives. |
Buy-Side Due Diligence Key Preparation Steps
When embarking on buy-side due diligence, adopting a growth-focused perspective can transform due diligence from a simple validation exercise into a strategic exploration.
Here’s how to approach the key preparation steps with an eye toward both identifying risks and uncovering growth opportunities:
Financial Review for Growth Potential
Objective: Beyond ensuring financial accuracy, delve into the financials to assess potential for scaling, cost efficiencies, and new revenue streams.
Actions: Analyze historical financial performance for growth trends, profitability margins, and cash flow health. Look for underexploited assets or areas where operational efficiencies could unlock additional value.
Operational Analysis for Efficiency and Scalability
Objective: Evaluate the target’s operational processes not just for current efficiency but for scalability and innovation potential.
Actions: Assess the company’s use of technology, supply chain logistics, and workforce productivity. Identify areas where improvements could lead to significant cost savings or enhanced operational capacity.
Legal and Compliance as a Foundation for Expansion
Objective: Ensure legal and regulatory compliance while evaluating how existing frameworks could support or hinder future growth.
Actions: Review contracts, licenses, and compliance records with a focus on scalability. Understand any restrictions that could impact future expansion plans or strategic pivots.
Market and Competitive Analysis for Strategic Positioning
Objective: Analyze the market and competitive landscape not only to understand the target’s current position but also to identify untapped opportunities and potential for market share growth.
Actions: Conduct a thorough market analysis to spot trends, emerging markets, and competitor weaknesses. Evaluate the target’s product or service offerings for differentiation and potential for expansion.
Assessing Strategic Fit and Synergies
Objective: Look beyond immediate strategic fit to potential synergies that could drive growth and enhance the combined entity’s competitive advantage.
Actions: Identify areas where the target company’s strengths complement your own. Explore opportunities for cross-selling, geographical expansion, and leveraging combined technological assets.
By incorporating these growth-focused strategies into the preparation steps of buy-side due diligence, investors not only protect their interests from potential risks but also lay the groundwork for post-acquisition growth and value creation.
This holistic approach ensures that the acquisition is not just safe but strategically advantageous, setting the stage for long-term success and scalability.
| Preparation Step | Objective | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Review | Assess growth potential and scalability. | Analyze financial trends, profitability, and areas for operational efficiency. |
| Operational Analysis | Evaluate for efficiency and scalability. | Assess technology use, supply chain logistics, and workforce productivity for improvements. |
| Legal and Compliance | Foundation for future expansion. | Review legal frameworks for scalability and potential restrictions on growth. |
| Market and Competitive Analysis | Identify opportunities for strategic positioning and market share growth. | Conduct market analysis, spot trends, and evaluate the competitive landscape. |
| Assessing Strategic Fit | Explore potential synergies for growth. | Identify complementarities, opportunities for cross-selling, and technological leverage. |
Benefits of Thorough Buy-Side Due Diligence
Conducting detailed buy-side due diligence is a critical and strategic step in the acquisition process, offering a significant advantage that can profoundly impact the success of your investment.
This process extends beyond identifying potential deal-breakers, providing a strategic edge through deep insights and thorough analysis.
Here’s how it makes a difference:
Increased Chances of a Successful Acquisition
Thorough due diligence enhances the likelihood of a successful acquisition by allowing investors to deeply understand the financial, operational, legal, and market aspects of the target company.
This comprehensive insight acts as a filter, helping to identify and avoid problematic investments while focusing on those with strategic value.
Identification of Potential Risks and Opportunities
One of the core benefits of buy-side due diligence is its dual focus on uncovering both risks and untapped opportunities.
While risks might include financial liabilities or operational inefficiencies, the process also shines a light on possibilities for growth, efficiency improvements, and market expansion.
This balanced view allows for better negotiation, effective integration planning, and a higher potential return on investment.
Facilitation of Strategic Planning and Decision Making
The detailed insights gained from due diligence are invaluable for strategic planning.
They provide a clear picture of the target’s market position and competitive landscape, enabling informed decisions on integration and future growth strategies.
This level of understanding is crucial for identifying synergies and planning how to leverage the acquisition for competitive advantage.
Enhancing Post-Acquisition Integration and Value Creation
A thorough due diligence process not only identifies synergies and potential for value creation but also offers a roadmap for effective post-acquisition integration.
By understanding the operational, cultural, and strategic nuances of the target company, investors can ensure a smoother integration process, realizing the anticipated value more efficiently.
Strategic Advantage in Competitive Markets
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, a comprehensive understanding of a potential acquisition can provide a significant strategic edge.
By uncovering unique growth opportunities and strategic fits that competitors might overlook, investors can secure deals that offer substantial long-term benefits, positioning themselves advantageously in the market.
In essence, thorough buy-side due diligence is indispensable for any serious buyer or investor. It goes beyond mitigating risks to unearth strategic opportunities, enabling more informed decision-making and negotiations.
The process ensures that investments not only align with current strategic goals but also set the stage for future growth and success.
Exploring Sell-Side Due Diligence
Definition of Buy-Side Due Diligence
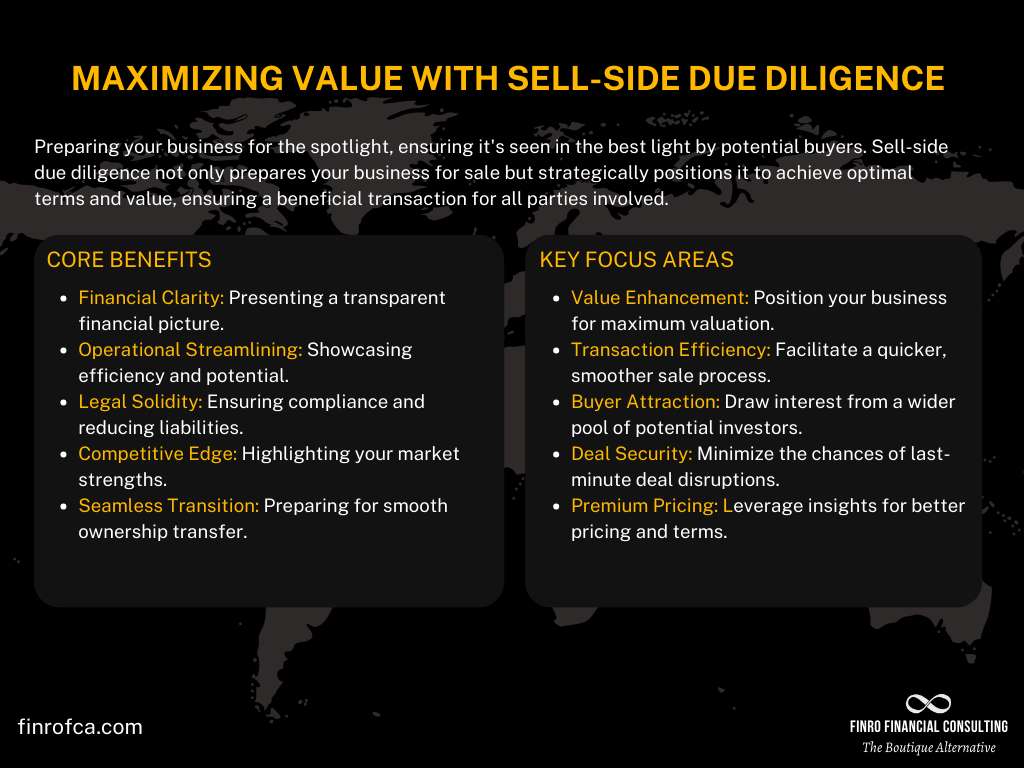
Sell-side due diligence is the process initiated by sellers or current business owners who are looking to sell their company or attract significant investments.
This proactive approach is all about meticulously preparing and presenting the business in its best possible light. It involves conducting a thorough review of the company’s financial health, operational efficiencies, legal compliances, and market position with the goal of identifying and addressing any potential issues that could deter buyers or decrease the business's value.
The purpose of sell-side due diligence is twofold.
First, it aims to ensure that the business is presented accurately and attractively, maximizing its appeal to potential buyers or investors. By highlighting strengths, clarifying financials, and resolving any outstanding issues beforehand, sellers can foster a smoother transaction process.
Second, it serves as a strategic move to potentially speed up the sale process and achieve a better valuation, as it reduces the uncertainties and risks for the buyer, making the investment more attractive from the outset.
In essence, sell-side due diligence is about taking control of the narrative around your business's sale or investment process.
It's an opportunity to fix what can be improved, highlight what shines, and ensure that the transition to new ownership or partnership is as seamless and beneficial as possible for all parties involved.
Sell-Side Due Diligence: Key Preparation Steps
When embarking on sell-side due diligence, the preparation is key to ensuring a smooth and successful transaction. Sellers must focus on several critical areas to enhance the business's appeal and value.
Here’s a closer look at these essential steps:
Financial Records Accuracy and Transparency
Accuracy in financial documentation is the cornerstone of sell-side due diligence. Ensuring that all financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, are accurate, up-to-date, and transparent is crucial.
This not only builds trust with potential buyers but also provides a clear picture of the financial health of the business.
Operational Improvements and Efficiency
Efficient operations are attractive to buyers as they often signal a well-run, profitable business.
Identifying areas where operations can be streamlined or improved—be it through process optimization, technology upgrades, or team restructuring—can significantly enhance the operational efficiency and, by extension, the value of the business.
Legal Standings and Regulatory Compliance
A clean legal bill of health is imperative.
Sellers need to ensure that the business is in compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, and that there are no outstanding legal issues or disputes.
This includes having all necessary licenses and permits in place and being up-to-date with regulatory requirements specific to the industry.
Competitive Advantage and Market Positioning
Understanding and articulating the business's unique value proposition and market positioning is key.
This involves a deep dive into the business’s competitive advantages, market share, customer base, and industry standing.
Clearly outlining what sets the business apart from its competitors can make it more attractive to potential buyers.
Planning for Transition and Investor Involvement
Anticipating the needs and concerns of potential buyers or investors regarding the transition phase post-acquisition is important.
Sellers should have a clear plan for how the business will continue to operate during and after the transition to new ownership.
This may include strategies for integrating the business into a larger portfolio, maintaining key personnel, and ensuring continuity of operations and customer service.
By meticulously addressing these key preparation steps, sellers can significantly improve the prospects of their business sale or investment round.
It’s about showcasing the business in the best possible light, reducing any perceived risk for the buyer, and smoothing the path to a successful deal closure.
| Preparation Area | Key Actions |
|---|---|
| Financial Records | Ensure all financial statements are accurate, up-to-date, and transparent. |
| Operational Improvements | Identify and implement ways to enhance operational efficiency and profitability. |
| Legal Standings | Confirm compliance with laws, resolve disputes, and secure necessary licenses and permits. |
| Competitive Advantage | Clearly articulate the business's unique value and position in the market. |
| Transition Planning | Develop a clear plan for smooth operation during and after the transition to new ownership or investment. |
Advantages of Conducting Sell-Side Due Diligence
Conducting thorough sell-side due diligence before initiating the sale process or seeking investment offers a range of benefits that can significantly impact the success of the transaction.
Understanding these advantages can help sellers and their advisors strategize effectively to maximize the business's value and attractiveness to potential buyers. Here are the key benefits:
Enhancing Business Appeal and Value
One of the primary advantages of comprehensive sell-side due diligence is the ability to enhance the overall appeal and value of the business.
By identifying and addressing any issues that could deter buyers or devalue the business, sellers can present their company in the best possible light.
This preparation often leads to a smoother sales process, fewer negotiations over price reductions, and the potential for a higher selling price.
Smoothing the Transaction Process
Sell-side due diligence helps to streamline the sales process by preparing the business thoroughly before it goes to market.
This proactive approach can reduce the time it takes to complete a sale by minimizing the back-and-forth typically associated with buyer due diligence.
With all information ready and transparently presented, buyers can make quicker decisions, accelerating the path to closing.
Attracting More Potential Buyers or Investors
A well-prepared business is more likely to attract a wider pool of potential buyers or investors.
By demonstrating that the business is well-managed, financially stable, and free of legal encumbrances, sellers can increase interest from high-quality buyers. This competitive interest can lead to better offers and more favorable terms for the seller.
Reducing Risks of Deal Falling Through
By addressing potential deal breakers upfront, sellers can significantly reduce the risk of transactions falling through at advanced stages.
Comprehensive sell-side due diligence uncovers and resolves issues before they become obstacles in negotiations, ensuring that deals progress more smoothly towards completion.
Commanding a Higher Price or Valuation
Finally, thorough sell-side due diligence can directly impact the financial outcome of the sale. By clearly documenting the business’s strengths, operational efficiencies, and growth potential, sellers can justify a higher asking price or valuation.
This detailed preparation provides a strong foundation for negotiations, highlighting the value and potential of the business to prospective buyers.
In conclusion, sell-side due diligence is not just a step in the preparation for selling a business or seeking investment; it's a strategic tool that can significantly enhance the outcome of the transaction.
By taking control of the due diligence process, sellers can navigate the sale more effectively, achieving better results and maximizing the return on their investment.
Key Differences Between Buy-Side and Sell-Side Due Diligence
Understanding the distinctions between buy-side and sell-side due diligence illuminates the strategic nuances each party brings to the transaction process.
These differences are crucial for tailoring the approach to due diligence effectively, ensuring that both buyers and sellers can optimize their outcomes.
Point of View: Perspective and Motivations
Buy-Side Due Diligence: Conducted by potential buyers or investors, the focus is on protecting their interests. The primary motivation is to uncover any hidden risks or issues that could impact the investment's value negatively. Buyers are looking to validate the information presented by the seller and ensure the investment aligns with their strategic objectives.
Sell-Side Due Diligence: Initiated by the seller, the aim is to present the business in the best possible light to potential buyers. Sellers are motivated to identify and address any potential deal-breakers before they go to market, enhancing the attractiveness and perceived value of the business. The goal is to streamline the sale process, attract the best possible offers, and justify a higher valuation.
Timing: When Due Diligence Occurs
Buy-Side Due Diligence: Typically begins after a preliminary agreement or interest is expressed by the buyer. It is a detailed examination that occurs before finalizing the transaction to ensure the buyer is making a well-informed decision.
Sell-Side Due Diligence: Usually starts before the business is even listed for sale or seeks investment. Conducting due diligence early allows sellers to proactively identify and rectify any issues that could impede a sale or reduce the business’s value.
Control and Initiative
Buy-Side Due Diligence: The buyer initiates and controls the due diligence process. This control allows the buyer to dive deeply into the areas of most concern or interest, dictating the scope and depth of the investigation based on their priorities and the information disclosed by the seller.
Sell-Side Due Diligence: The seller takes the initiative, conducting a self-assessment of their business with or without the assistance of external advisors. This proactive approach lets the seller control the narrative by addressing issues before they can become sticking points in negotiations, and ideally, enhancing the business's appeal to potential buyers.
In summary, the main differences between buy-side and sell-side due diligence revolve around who is conducting the investigation, their underlying motivations, the timing of the process, and who holds control over the initiative.
Understanding these distinctions helps both buyers and sellers navigate the transaction process more effectively, ensuring that their respective needs and objectives are met.
| Aspect | Buy-Side Due Diligence | Sell-Side Due Diligence |
|---|---|---|
| Point of View | Focused on protecting buyer’s interests. | Aimed at presenting the business in the best light to attract buyers. |
| Timing | Occurs after preliminary interest but before finalizing the transaction. | Initiated before the business is listed for sale or seeks investment. |
| Control and Initiative | Controlled by the buyer, allowing a deep dive into areas of concern. | Initiated by the seller to proactively address potential issues. |
Conclusion
Due diligence emerges as the critical element that can make or break a deal.
Whether you're on the buy side, meticulously examining a potential investment to safeguard your interests and uncover strategic opportunities, or on the sell side, preparing your business to showcase its best attributes and maximize value, understanding the nuances of due diligence is paramount.
The distinction between buy-side and sell-side due diligence lies not just in their objectives but in their timing, control, and strategic focus. Buy-side due diligence is a deep dive, initiated by potential buyers to uncover any and all facets of a business that could impact their investment.
It's a protective measure that also holds the promise of discovering untapped potential for growth. On the flip side, sell-side due diligence is a proactive showcase, a preparation by sellers to ensure their business is viewed in the best possible light, aiming to smooth the path to a successful and profitable sale.
These processes, while distinct, are not adversarial but complementary. They represent the yin and yang of business transactions, each serving to ensure that when a deal closes, it's not just a transaction but a mutually beneficial strategic alignment.
For buyers, due diligence affords the confidence to proceed with an acquisition, armed with comprehensive insights into the potential risks and rewards. For sellers, it offers the chance to address any issues head-on, present their business optimally, and achieve a valuation that reflects its true worth.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, the role of due diligence in facilitating successful, strategic acquisitions and sales becomes increasingly crucial. Whether you're buying or selling, the key to a favorable outcome lies in a meticulous, informed approach to due diligence, emphasizing the need for thoroughness and attention to detail.
By embracing both the protective scrutiny of the buy-side and the preparatory thoroughness of the sell-side, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of business transactions with greater assurance and strategic insight, turning potential deals into opportunities for sustainable growth and success.
Key Takeaways
Due Diligence is Essential: Protects interests, uncovers risks and opportunities, ensuring informed decisions in business transactions.
Buy-Side Focus: Identifies potential investment risks and strategic growth opportunities, safeguarding buyer interests.
Sell-Side Preparation: Enhances business appeal and value, addressing issues proactively to attract better offers.
Strategic Timing and Control: Buy-side initiated post-interest; sell-side starts pre-listing, each controlling their due diligence process.
Mutual Benefits: Facilitates successful, mutually beneficial transactions, combining protective scrutiny and preparatory thoroughness.
Answers to The Most Asked Questions
-
Sell-side due diligence is initiated by the seller to prepare the business for sale. It aims to present the business in the best possible light, addressing any potential issues to enhance attractiveness and value, and to facilitate a smooth transaction process.
-
The two main types are buy-side and sell-side due diligence. Buy-side due diligence is conducted by potential buyers or investors to protect their interests and ensure an informed investment decision. Sell-side due diligence is conducted by sellers to prepare and present their business optimally for sale.
-
The key differences lie in perspective, timing, and control. Buy-side due diligence is focused on protecting the buyer's interests, uncovering risks, and identifying growth opportunities, typically occurring after preliminary interest. Sell-side due diligence, on the other hand, is aimed at presenting the business favorably to attract buyers or investors, starting before the business is listed for sale. The buyer controls the buy-side process, while the seller initiates and controls the sell-side process.
-
In mergers and acquisitions (M&A), "sell-side" refers to the party (usually the business owner or shareholders) looking to sell their company or business unit. The sell-side engages in preparing the business for sale, including conducting sell-side due diligence, to maximize the business’s appeal and value to potential buyers.