Understanding The Cost of Revenues
By Lior Ronen | Founder, Finro Financial Consulting
Understanding the cost of revenues is essential for any business looking to stay competitive and profitable. Whether you’re reviewing financial projections or making pricing decisions, knowing exactly what your costs are—and how they impact your bottom line—can make all the difference.
The cost of revenues refers to the total expense required to produce or deliver your product or service. It includes everything from materials and labor to overhead costs like rent and utilities. By breaking down these components, you'll gain a clearer picture of how your business operates financially and where adjustments can be made to improve profitability.
In this article, we’ll cover what the cost of revenues includes, how to calculate it, and why it plays a key role in your overall financial strategy.
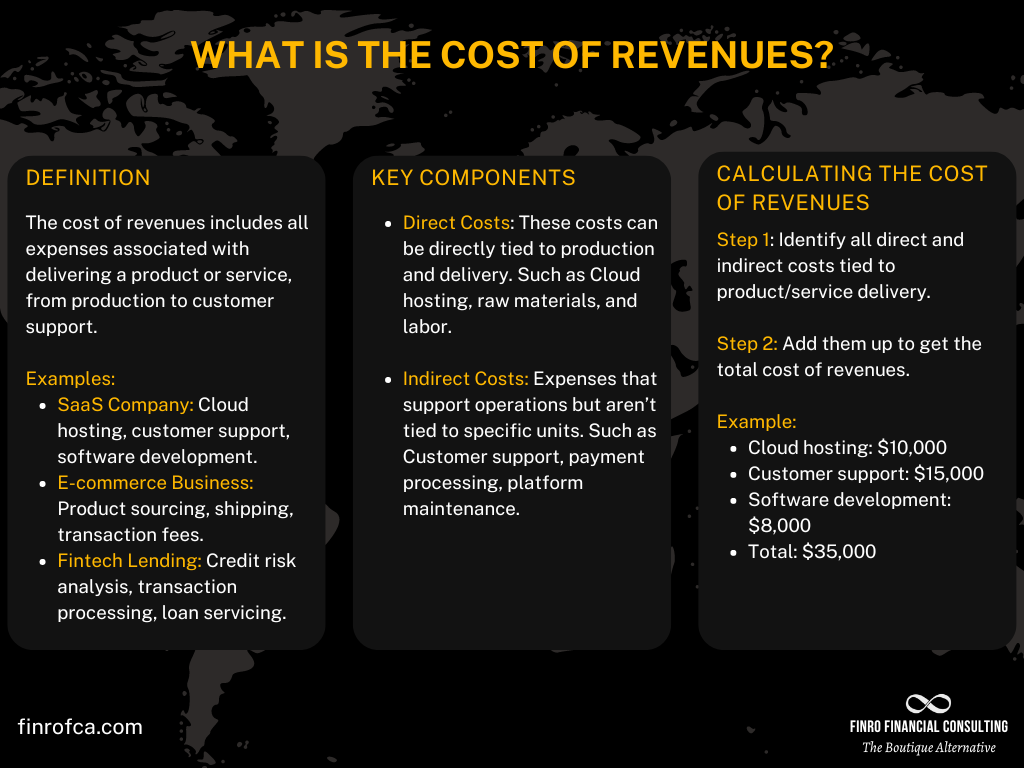
The cost of revenues includes all expenses involved in delivering a product or service, including both direct and indirect costs. For tech companies, it’s a critical metric that affects gross profit, operating profit, and overall financial health.
Effective management of these costs can improve profitability through strategies like optimizing cloud usage, automating support, and refining payment processing. Achieving a balance between cost efficiency and maintaining product quality is key to sustainable growth, ensuring that every dollar spent contributes to delivering value while maintaining competitive margins.
What is the Cost of Revenues?
In tech companies, the cost of revenues plays a crucial role in understanding the financial health of the business. It goes beyond simple production costs and includes all expenses related to delivering your product or service to the customer.
Accurately calculating and managing this cost is key to maintaining profitability and operational efficiency.
The cost of revenues includes all the direct and indirect costs a company incurs to generate its sales or deliver its services. For tech companies, these costs can range from hosting and development fees to customer service and transaction processing.
While often confused with the cost of goods sold (COGS), which primarily refers to the production of physical goods, the cost of revenues in tech businesses encompasses the full scope of delivering digital or service-based offerings.
How Is the Cost of Revenues Calculated?
The cost of revenues is calculated by adding up all the expenses directly tied to delivering your product or service. This could include:
Direct costs like cloud hosting, software development, or product sourcing.
Indirect costs such as customer support, payment processing, and platform maintenance.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say you run a SaaS company that provides a subscription-based project management tool. Here’s a breakdown of your cost of revenues for a given month:
Cloud Hosting (AWS): $10,000
Customer Support Team Salaries: $15,000
Third-Party Integrations (e.g., payment processors): $2,000
Ongoing Software Development Costs: $8,000
In this case, the total cost of revenues for the month would be the sum of all these expenses:
Total Cost of Revenues = $10,000 + $15,000 + $2,000 + $8,000 = $35,000
This $35,000 represents the total expenses incurred to keep your SaaS platform operational and deliver value to your customers. Once you subtract this cost from your monthly revenue, you can determine your gross profit.
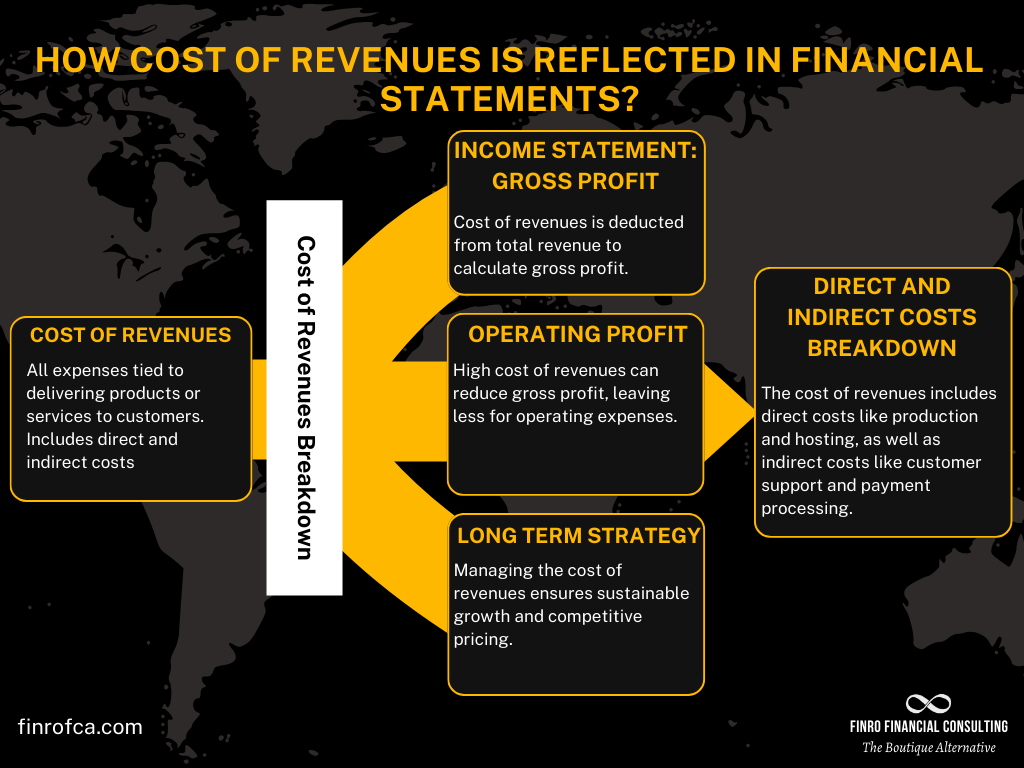
Income Statement Placement and Financial Impact
On the income statement, the cost of revenues sits right below revenues and directly impacts the company’s gross profit, which is the difference between total revenues and the cost of revenues. The more efficiently a company manages these costs, the higher its gross profit.
Beyond gross profit, the cost of revenues also affects operating profit (or operating income). After gross profit, operating expenses such as R&D, sales and marketing, and administrative costs are subtracted, leaving operating income. If the cost of revenues is too high, both gross and operating profits will shrink, limiting the company’s ability to reinvest in growth or maintain healthy margins.
In tech companies, keeping the cost of revenues in check is critical to scaling operations while maintaining profitability. Mismanaging these costs can erode profit margins and hurt long-term business performance.
Real-World Examples of the Cost of Revenues
To understand the cost of revenues in tech businesses, let’s look at three real-world cases: SaaS companies, e-commerce platforms, and fintech lending firms. Each faces different challenges and costs associated with delivering their services.
SaaS Companies
In a SaaS (software-as-a-service) company, the cost of revenues typically includes:
Cloud Hosting Fees: The cost of maintaining servers and storage to keep the platform running 24/7.
Customer Support: Teams or automated systems to assist users with technical issues.
Software Development: Ongoing development to update features, fix bugs, and improve performance.
Third-Party Integrations: Services like payment gateways or security tools that help deliver the platform.
For example, a SaaS company providing project management software might spend heavily on cloud infrastructure (e.g., AWS) and customer success teams to ensure users remain satisfied with their service. All these expenses contribute to the cost of revenues.
E-Commerce Companies
For an e-commerce business, the cost of revenues includes:
Product Sourcing: The cost of acquiring the goods being sold.
Shipping and Fulfillment: Fees associated with warehousing, packaging, and delivering products to customers.
Payment Processing: Transaction fees from payment gateways like Stripe or PayPal.
Customer Service: Handling inquiries, returns, and complaints.
For instance, if an online clothing store sells t-shirts, their cost of revenues would cover not just the production of the t-shirts, but also shipping, payment processing fees, and customer support operations.
Fintech Lending Companies
In a lending fintech company, the cost of revenues can include:
Credit Risk Analysis: The cost of assessing borrowers' creditworthiness, often through data-driven algorithms or third-party credit scoring services.
Transaction Processing: Handling payments, loan disbursements, and collections.
Loan Servicing: Managing the loan after it’s issued, which includes customer support, compliance, and payment tracking.
For example, a fintech company offering short-term loans would have credit risk analysis systems as part of their cost of revenues, along with ongoing costs related to maintaining the lending platform and servicing loans.
Understanding the cost of revenues across different tech sectors highlights its importance in shaping gross and operating profit. Whether you run a SaaS business, an e-commerce platform, or a fintech company, keeping a close eye on these costs is key to maintaining financial health and improving profit margins.
| Type of Company | Key Components of Cost of Revenues | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| SaaS Company | Cloud hosting, customer support, software development, third-party services | AWS hosting fees, customer success team salaries, subscription billing tools |
| E-commerce Company | Product sourcing, shipping and fulfillment, payment processing, customer service | Product cost, shipping fees, PayPal/Stripe fees, returns management |
| Fintech Lending Company | Credit risk analysis, transaction processing, loan servicing, customer support | Credit scoring services, loan platform maintenance, collections support |
Income Statement Placement and Financial Impact
Understanding where the cost of revenues sits on the income statement is key to analyzing a company's profitability.
In tech companies, this metric has a direct impact on two important measures: gross profit and operating profit.
How Is It Reflected on the Income Statement?
The cost of revenues appears right below the revenue line on the income statement. This allows you to see how much of the revenue is spent on the costs associated with delivering your product or service. Subtracting the cost of revenues from total revenue gives you the company’s gross profit.
Gross Profit Calculation:
Formula: Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Revenues
Example: If a SaaS company earns $100,000 in monthly subscription revenue and incurs $35,000 in costs related to cloud hosting, customer support, and software development, then:
Revenue: $100,000
Cost of Revenues: $35,000
Gross Profit: $100,000 - $35,000 = $65,000
Role in Operations and Profitability
The cost of revenues plays a significant role in assessing a company's operational efficiency and profitability:
Impact on Gross Profit:
Gross profit reflects how efficiently a company can turn revenue into profit after covering the costs of delivering its services or products. A lower cost of revenues typically means a higher gross profit, allowing the business to reinvest in growth, such as improving its product or expanding into new markets.Impact on Operating Profit:
After calculating gross profit, the next step is to subtract operating expenses (such as research and development, sales and marketing, and administrative expenses) to determine operating profit. High costs of revenues can eat into gross profit, reducing the amount left over for these critical expenses and ultimately impacting the company’s operating income.Long-Term Strategy:
Understanding and managing the cost of revenues is essential for long-term strategic planning. It allows tech companies to identify areas where they can reduce costs without sacrificing service quality, helping them maintain competitive pricing while improving margins.
For tech companies, especially those delivering digital services, keeping a close eye on the cost of revenues can be the difference between scalable growth and stagnation.
Mismanagement of these costs can lead to shrinking margins and limit a company’s ability to expand or adapt to market changes.
Optimizing the Cost of Revenues
Effectively managing the cost of revenues is crucial for tech companies looking to maintain healthy profit margins while delivering value to their customers.
By identifying areas for cost reduction and streamlining operations, companies can improve their gross margins without sacrificing the quality of their products or services.
Strategies for Cost Control
Optimize Cloud Infrastructure and Hosting
For SaaS companies, cloud hosting can be a significant portion of the cost of revenues. Optimizing server usage, negotiating better deals with cloud providers, or even adopting a multi-cloud strategy can help reduce these costs. For example, reviewing server capacity regularly to avoid paying for unused storage or computing power can save substantial amounts over time.Automate Customer Support
Customer support is often a major indirect cost, especially for companies that rely on high-touch customer success. Implementing AI chatbots or automated response systems can handle routine inquiries, reducing the need for a large support team. This allows human agents to focus on complex issues that require a personalized touch, resulting in a better balance between cost-efficiency and customer satisfaction.Refine Payment Processing Solutions
For e-commerce and fintech companies, transaction fees can quickly add up, especially as sales volume increases. Choosing payment processors with competitive rates and integrating them efficiently into the sales process can help reduce transaction costs. Some businesses may also benefit from negotiating volume-based pricing with payment service providers, leading to lower fees as they scale.Focus on Economies of Scale
As companies grow, they often achieve economies of scale, which means they can spread out fixed costs over a larger revenue base. This is especially relevant for tech companies with high upfront development costs but lower marginal costs for each additional customer. By scaling effectively, companies can reduce the cost of revenues as a percentage of sales, thereby improving profitability.Outsource Non-Core Functions
Outsourcing non-core functions, such as certain aspects of software development or back-office operations, can be an effective way to control costs. This allows tech companies to focus their resources on what they do best, while third-party providers handle other tasks at a potentially lower cost. This strategy is particularly useful for startups and smaller firms that might not have the internal bandwidth to manage all operational aspects.
Balancing Cost Management and Quality
It’s important to remember that reducing the cost of revenues should not come at the expense of product or service quality. Striking the right balance is key.
A SaaS company that cuts back too much on server capacity might see increased downtimes, impacting user experience and customer retention. Similarly, an e-commerce platform that skimps on customer support might end up with lower customer satisfaction and higher return rates.
Measuring the Impact of Optimization Efforts
Track Key Metrics: Regularly monitoring key financial metrics like gross margin, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and lifetime value (LTV) can help assess whether cost-saving efforts are having the desired impact.
Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Comparing your cost of revenues to industry benchmarks can highlight areas where your company might be overspending and opportunities for improvement.
Adjust Strategies as Needed: Optimization is an ongoing process. As market conditions change, companies should continuously evaluate their cost structure and adjust their strategies to remain competitive.
By implementing these strategies, tech companies can keep their cost of revenues in check, allowing them to reinvest in growth and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Get your expert support now!
Conclusion
Managing the cost of revenues is more than just a financial exercise—it's a strategic decision that directly impacts a company’s ability to thrive in a competitive market. For tech companies, where margins can be thin and competition fierce, understanding this metric is crucial for long-term success.
By breaking down the cost of revenues into direct and indirect components, companies can gain a clearer picture of their financial operations. This clarity enables them to make informed decisions about where to cut costs, where to invest more resources, and how to price their products or services effectively.
Whether it’s optimizing cloud infrastructure, automating customer support, or negotiating better rates with payment processors, there are many strategies that tech companies can use to keep their costs manageable. But, as always, these strategies must be implemented with care—reducing costs should not come at the expense of the customer experience or product quality.
Ultimately, keeping the cost of revenues in check is about finding the right balance. It’s about delivering the best possible product or service to your customers while ensuring that every dollar spent is driving value. By focusing on efficiency and maintaining a clear view of these expenses, tech companies can improve their gross and operating profits, paving the way for sustainable growth.